LeetCode 784. 字母大小写全排列
作者:Choi Yang
更新于:2 个月前
字数统计:711 字
阅读时长:3 分钟
阅读量:
题目描述
给定一个字符串 S,通过将字符串 S 中的每个字母转变大小写,我们可以获得一个新的字符串。返回所有可能得到的字符串集合。
示例:
javascript
输入:S = "a1b2"
输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
输入:S = "3z4"
输出:["3z4", "3Z4"]
输入:S = "12345"
输出:["12345"]输入:S = "a1b2"
输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
输入:S = "3z4"
输出:["3z4", "3Z4"]
输入:S = "12345"
输出:["12345"]提示:
javascript
S 的长度不超过12。
S 仅由数字和字母组成。S 的长度不超过12。
S 仅由数字和字母组成。来源:力扣(LeetCode)链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-case-permutation 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
这道题就是递归操作,没有回溯,是一个挺有意思的题目,在讲解思路之前,我先搬运一下大佬的图解,方便我后续补充。
第一步

第二步
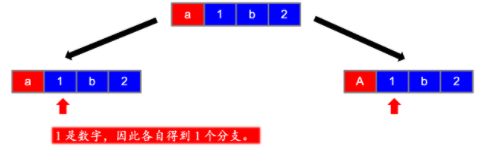
第三步
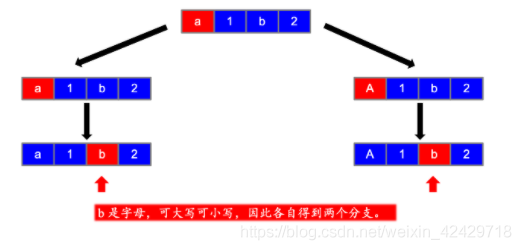
第四步
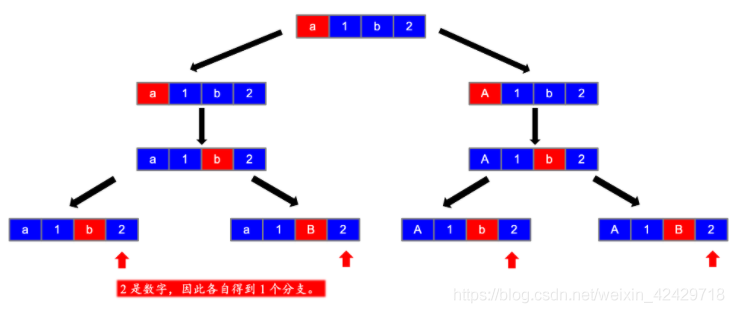
第五步
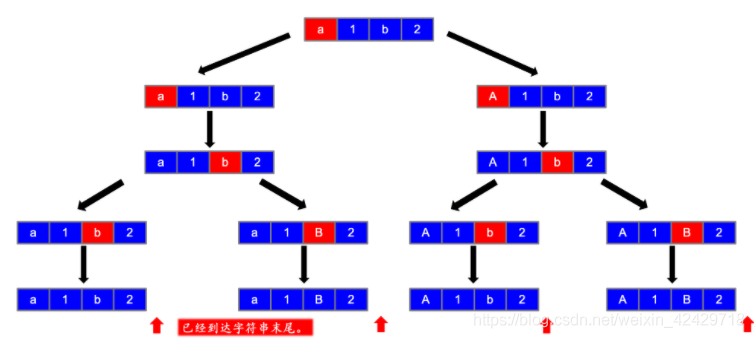
第六步
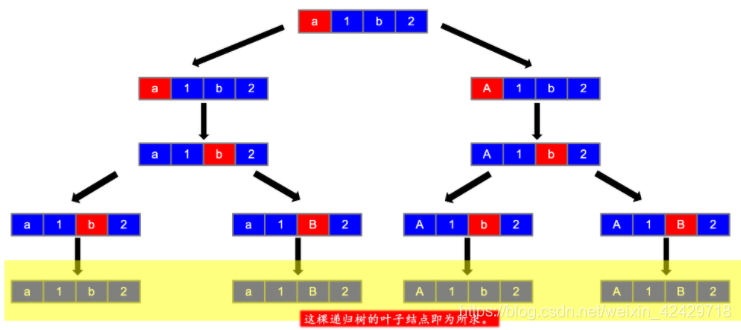
好了,有了上述图解之后(还是感谢大佬的图解,万分感谢 orz),我相信明白的已经明白了,如果不明白我继续解释。
此题我们只需要从头往后遍历一遍即可,对于非字母节点,我们只会产生一个分支,而对于字母节点,我们可以产生两个分支,即大写字母和小写字母。(详细请参见下述代码)
于是,我们只要简单搜一遍就可以了。
javascript
/**
* @param {string} S
* @return {string[]}
*/
var letterCasePermutation = function (S) {
let res = [];
let dfs = (t, str) => {
if (t.length === S.length) return res.push(t);
let ch = str[0];
let nextStr = str.substr(1);
// 当前位置为数字,只有一个分支
if (!isNaN(Number(ch))) {
dfs(t + ch, nextStr);
} else {
//当前位置为字母,会产生两个分支
let tmp = ch.toUpperCase();
if (tmp === ch) tmp = ch.toLowerCase();
dfs(t + ch, nextStr);
dfs(t + tmp, nextStr);
}
};
dfs("", S);
return res;
};/**
* @param {string} S
* @return {string[]}
*/
var letterCasePermutation = function (S) {
let res = [];
let dfs = (t, str) => {
if (t.length === S.length) return res.push(t);
let ch = str[0];
let nextStr = str.substr(1);
// 当前位置为数字,只有一个分支
if (!isNaN(Number(ch))) {
dfs(t + ch, nextStr);
} else {
//当前位置为字母,会产生两个分支
let tmp = ch.toUpperCase();
if (tmp === ch) tmp = ch.toLowerCase();
dfs(t + ch, nextStr);
dfs(t + tmp, nextStr);
}
};
dfs("", S);
return res;
};cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string S) {
vector<string> res;
dfs(res, S, 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<string>& res, string& S, int i) {
if (i == S.size()) {
res.push_back(S);
return;
}
dfs(res, S, i + 1);
if (!isalpha(S[i])) return;
S[i] ^= (1 << 5);
dfs(res, S, i + 1);
S[i] ^= (1 << 5);
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string S) {
vector<string> res;
dfs(res, S, 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<string>& res, string& S, int i) {
if (i == S.size()) {
res.push_back(S);
return;
}
dfs(res, S, i + 1);
if (!isalpha(S[i])) return;
S[i] ^= (1 << 5);
dfs(res, S, i + 1);
S[i] ^= (1 << 5);
}
};java
class Solution {
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(res, S.toCharArray(), 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(List<String> res, char[] chs, int i) {
if (i == chs.length) {
res.add(new String(chs));
return;
}
dfs(res, chs, i + 1);
if (!Character.isLetter(chs[i])) return;
chs[i] ^= (1 << 5);
dfs(res, chs, i + 1);
chs[i] ^= (1 << 5);
}
}class Solution {
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(res, S.toCharArray(), 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(List<String> res, char[] chs, int i) {
if (i == chs.length) {
res.add(new String(chs));
return;
}
dfs(res, chs, i + 1);
if (!Character.isLetter(chs[i])) return;
chs[i] ^= (1 << 5);
dfs(res, chs, i + 1);
chs[i] ^= (1 << 5);
}
}python
class Solution:
def letterCasePermutation(self, S: str) -> List[str]:
res = []
self.dfs(res, S, 0)
return res
def dfs(self, res, S, i):
if i == len(S):
res.append(S)
return
self.dfs(res, S, i + 1)
if not S[i].isalpha(): return
S = S[:i] + chr(ord(S[i]) ^ (1 << 5)) + S[i + 1:]
self.dfs(res, S, i + 1)
S = S[:i] + chr(ord(S[i]) ^ (1 << 5)) + S[i + 1:]class Solution:
def letterCasePermutation(self, S: str) -> List[str]:
res = []
self.dfs(res, S, 0)
return res
def dfs(self, res, S, i):
if i == len(S):
res.append(S)
return
self.dfs(res, S, i + 1)
if not S[i].isalpha(): return
S = S[:i] + chr(ord(S[i]) ^ (1 << 5)) + S[i + 1:]
self.dfs(res, S, i + 1)
S = S[:i] + chr(ord(S[i]) ^ (1 << 5)) + S[i + 1:]javascript
学如逆水行舟,不进则退学如逆水行舟,不进则退